Algorithm Homework:
If $x\sin(\pi x) = \int_0^{x^2}f(t)dt$, where $f$ is a continuous function, find $f(4)$.
Answer
Let $F(x)$ be an antiderivative of $f(t)$, so $\int_0^{x^2}f(t)dt = F(x^2)-F(0)$ by the fundamental theorem of Calculus. Apply differentiation to $x$ on the integral, we get $\frac{d}{dx}\left(\int_0^{x^2}f(t)dt\right) = F’(x^2)\cdot 2x = 2xf(x^2)$. On the other hand $(x\sin(\pi x))’ = \sin(\pi x) + \pi x\cos(\pi x)$. By setting $x=2$, we conclude that $f(4) = \frac{\pi}{2}$.
Suppose $f$ is continuous, $f(0)=0$, $f(1)=1$, $f’(x)>0$, and $\int_0^1f(x)dx=\frac{1}{3}$. Find the value of the integral $\int_0^1f^{-1}(y)dy$.
Answer
The following graph explains that the integral is $1-\frac{1}{3}$. The area of the red shadow part is the integral. 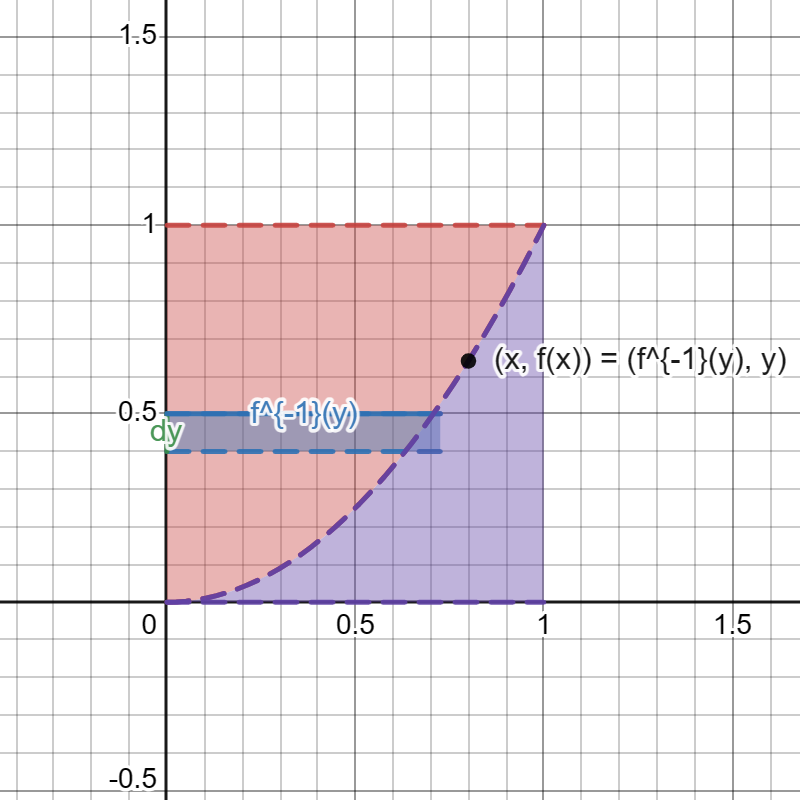
If $\int_0^4e^{(x-2)^4}dx=k$, find the value of $\int_0^4xe^{(x-2)^4}dx$.
Answer
Let $u=x-2$, then $x=u+2$. Thus, we have \(\int_{0}^4 x e^{(x-2)^4}dx = \int_{-2}^{2} (u+2)e^{u^4}du = \int_{-2}^{2}ue^{u^4}du + 2\int_{-2}^{2}e^{u^4}du.\) Since $ue^{u^4}$ is an odd function, the integral $\int_{-2}^{2}ue^{u^4}du$ is $0$ and $\int_{-2}^{2}e^{u^4}du = \int_0^4 e^{(x-2)^4}dx$. Hence, the desired integral is $2k$.
Evaluate \(\lim_{n\to\infty}\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{n}\sqrt{n+1}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{n}\sqrt{n+2}}+\cdots+\frac{1}{\sqrt{n}\sqrt{n+n}}\right).\)
Answer
We have \(\begin{align} \lim_{n\to\infty}\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{n}\sqrt{n+1}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{n}\sqrt{n+2}}+\cdots+\frac{1}{\sqrt{n}\sqrt{n+n}}\right) \\\\ = \lim_{n\to\infty}\left(\frac{1}{n}\sqrt{\frac{1}{1+1/n}} + \frac{1}{n}\sqrt{\frac{1}{1+2/n}} + \cdots + \frac{1}{n}\sqrt{\frac{1}{1+1}}\right). \end{align}\) This is the limit of the right Riemann sum of $R_n$ for the function $\frac{1}{1+x}$ from $0$ to $1$. Since this function is integrable, the limit of the right Riemann sum will converge to the integral $\int_0^1\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+x}}dx$. We then can conclude that the limit is $\left.\sqrt{1+x}\right|_{0}^1 = \sqrt{2}-1$.
-
Implement a Python program that calculates the left, right, and midpoint Riemann sums for a given function $f(x)$ over a specified interval $[a, b]$. Your program should allow the user to input the function, the interval, and the number of subintervals ($n$) they want to use for the Riemann sum. It should then compute and display the results for each type of Riemann sum (left, right, and midpoint).
-
Create a Python program that generates a random Riemann sum. This program should do the following:
- Generate random partition points $x_0, x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n$ that satisfy the condition $\max(x_{i+1} - x_i) < \delta$ for a given small positive value $\delta$, which also allows the user to select.
- Randomly select sample points $x_i^*$ within each subinterval.
- Evaluate the Riemann sum using these randomly generated values and display the result.